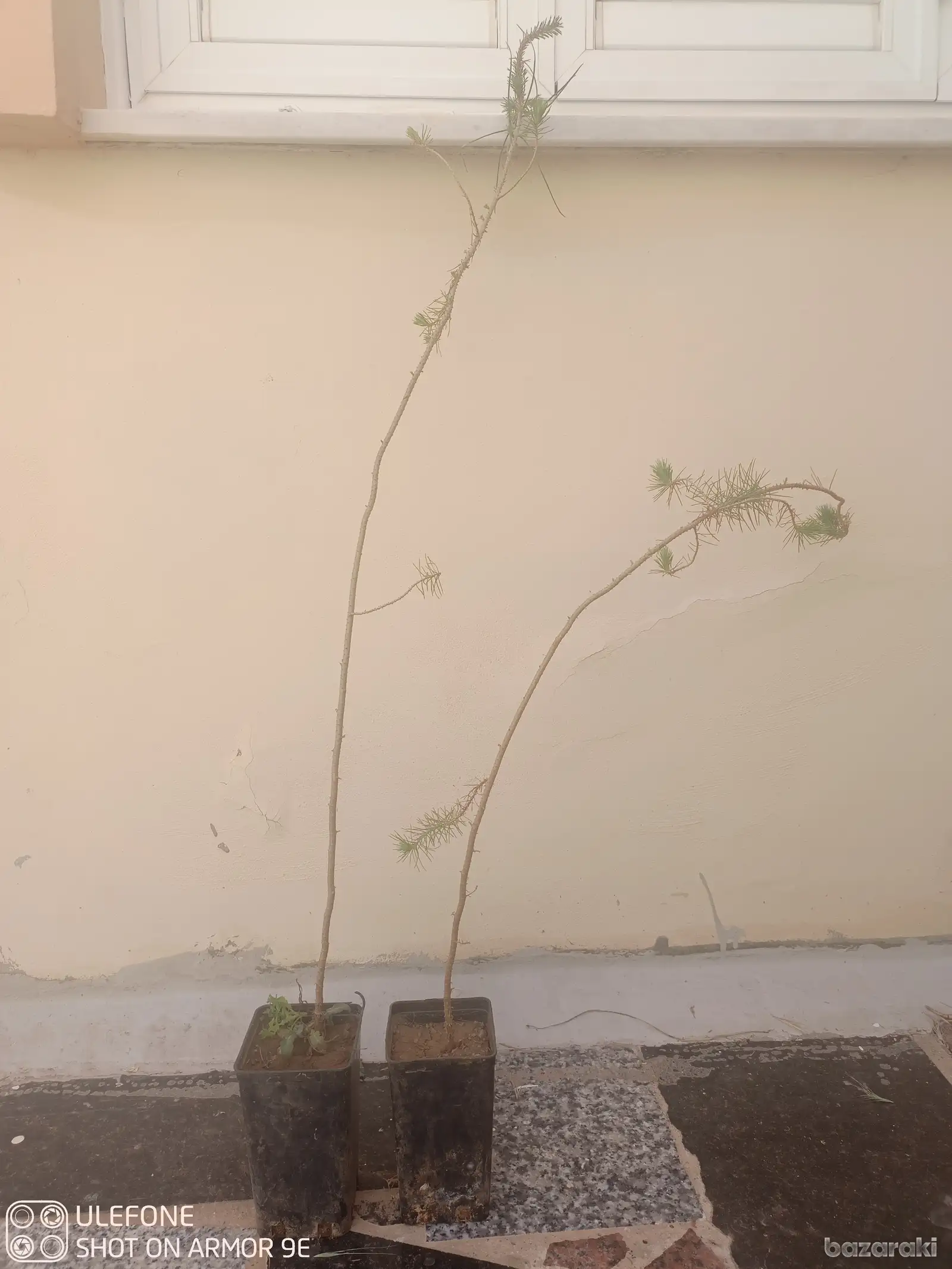
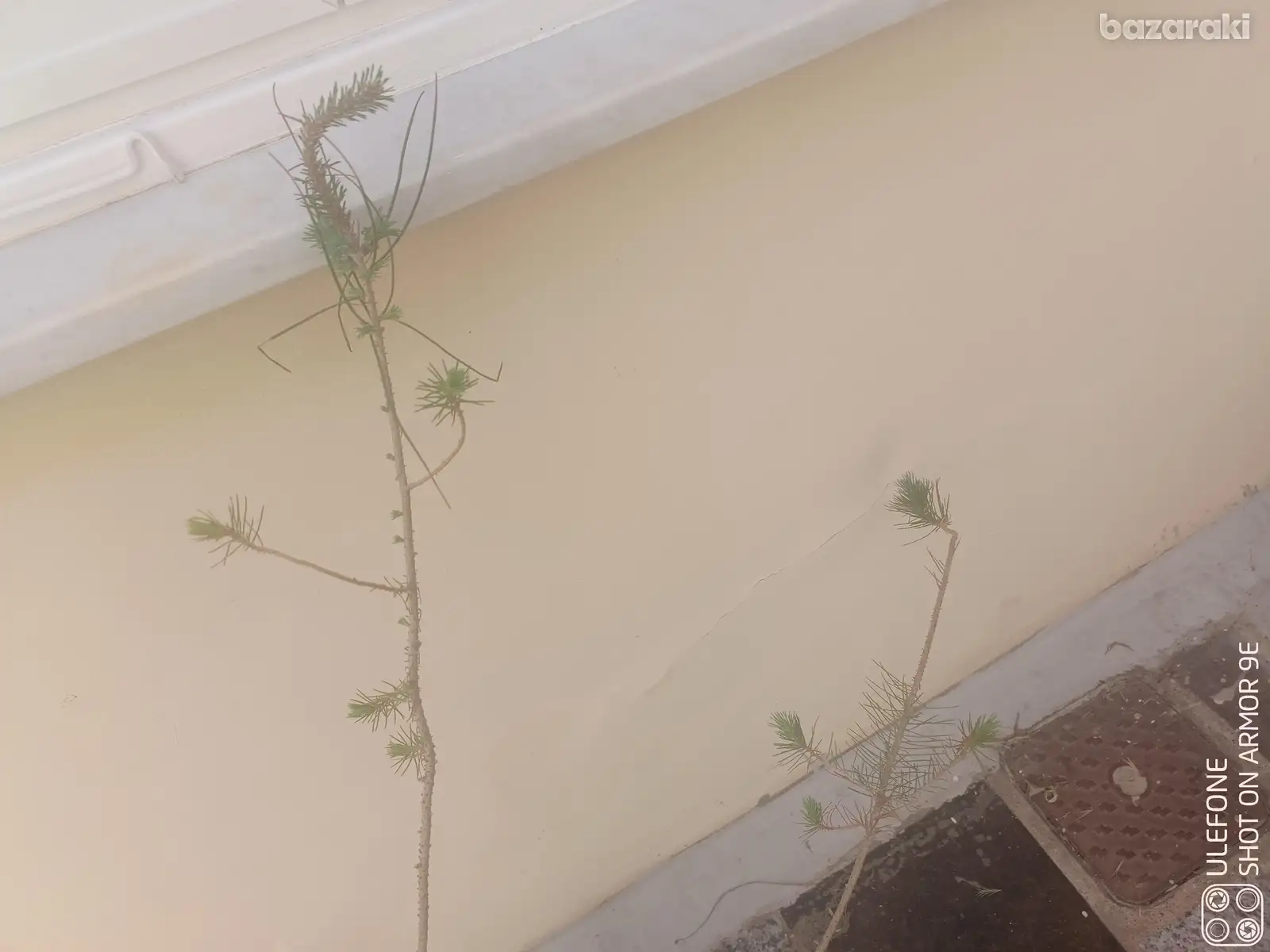
Pine pinus brutia plants for pine nuts, πεύκος φυτά για παραγωγή πινόλια



















- Κατάσταση: Καινούργιο
Pine pinus brutia plants for production of Pine Nuts, hot dry climates, Πεύκος Φυτά για παραγωγή Πινόλια
Plant Height: 1 metre, Ύψος φυτού: 1 μέτρο
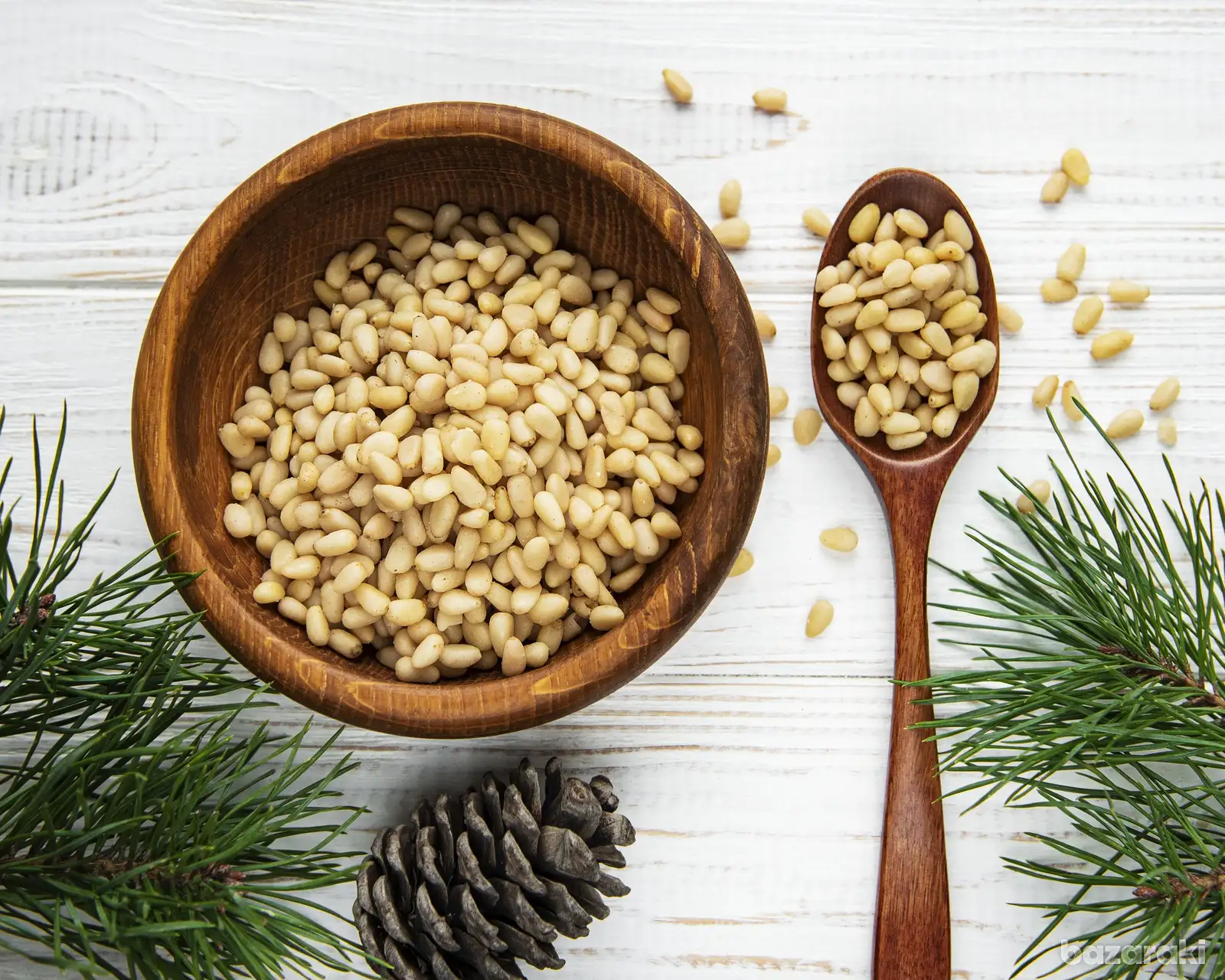
Pine nuts are edible kernels extracted from the seed of a variety of species of pine tree. The seeds are typically thick-shelled and grow inside of pine cones that look very similar to the pine cones that grow on other pines grown only for timber. Cone harvesting and extraction and preparation of the kernels are time-consuming and costly – contributing to the high prices at which pine nuts sell. Pine nuts are highly nutritious and keep well for many months if stored properly in dry, cool conditions and out of direct sunlight. They are extremely versatile in cooking due to their mild flavor, creamy and subtle when raw and richer and nuttier when lightly toasted. They add interest, flavour and texture to many sweet and savoury dishes. They are a truly natural product – essentially unchanged over many millenia – requiring no insecticides or fungicides to either grow the trees or prepare the kernels for market.
Nutrition
Pine nuts are wonderfully healthy and nutritious food. They are rich in the kind of healthy fats now considered to be important in a healthy diet. Fatty acids found in pine nuts include linoleic acid and pinolenic acid which both are the subject of research into their role in regulating blood pressure, suppressing appetite for those trying to control their weight and preventing and treating stomach ulcers. More surprising to some is that pine nuts are very rich in protein. Some studies have found at least trace amounts of every one of the 28 amino acids needed for human metabolism. The European stone pine nut has the highest protein content of all the nut pines at 34% by weight. As a result of the high protein content they have a lower oil content than other pine nuts (48% as against 65% for Chinese sourced nuts). They also contain antioxidants (including vitamins A, B, C, D, E and K as well as lutein) which are claimed to prevent disease and aging by eliminating free radicals. Pine nuts have almost no sodium, and contain useful amounts of other minerals such as calcium, magnesium, potassium, phosphorous and iron. And finally, they contain moderate amounts of dietary fibre.
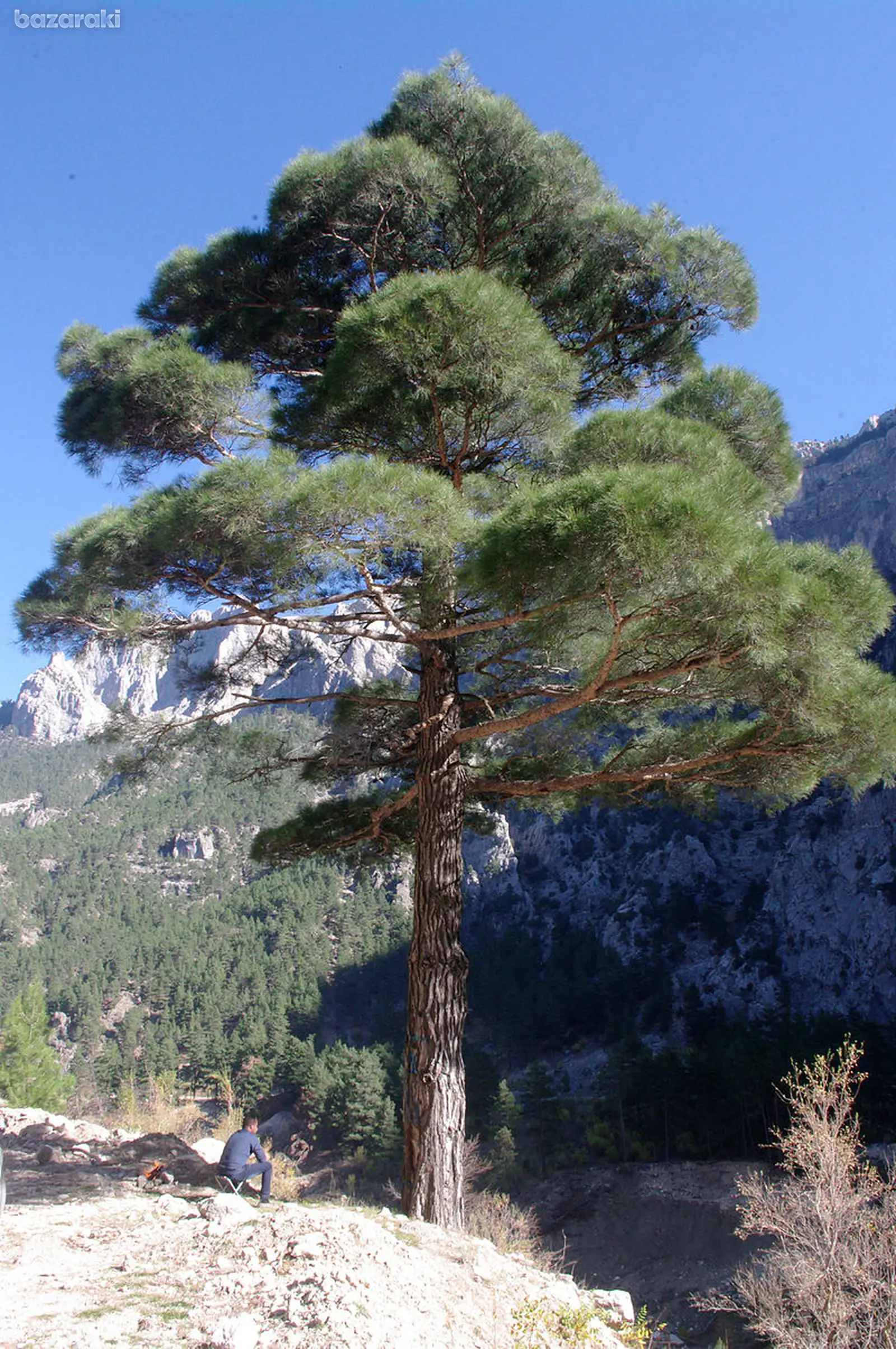
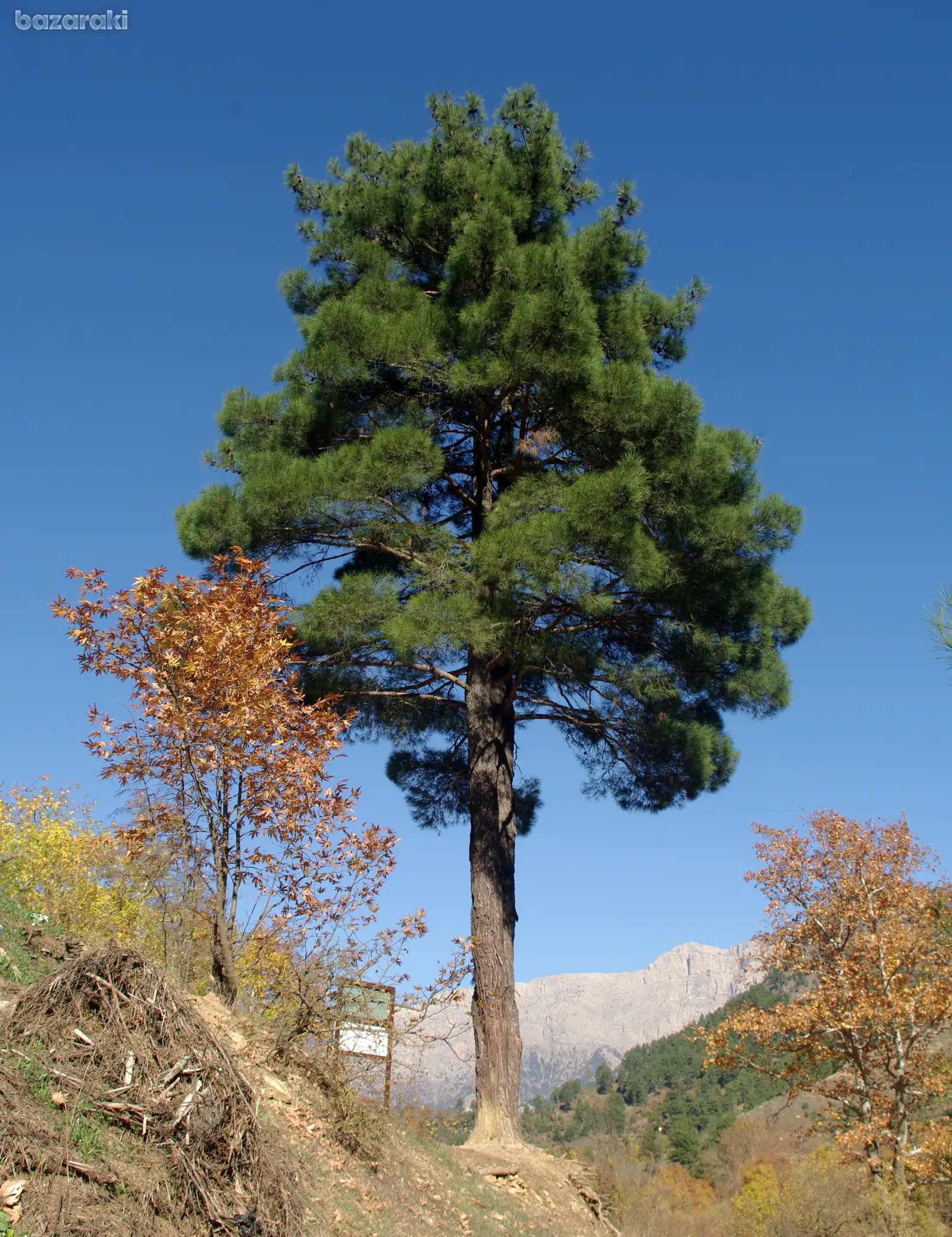
Brutia, Calabrian, or Turkish pine (Pinus brutia) is a fast growing, medium-sized, evergreen tree often associated with the related Aleppo pine (Pinus halepensis). The tree is native to the eastern Mediterranean and Aegean regions of Türkiye, and there are small, isolated populations along the Black Sea coast of Türkiye and Georgia (Kurt et al., 2012). The tree covers large areas on the coast of Türkiye where it is economically important as the main source of wood and forest cover and was widely planted for soil protection and windbreaks in the 1930s to 1970s. The tree is widely used in afforestation and reforestation programmes in southern and western Türkiye, where it covers 24% of the total forested area (Kandedmir, Kandemir, and Kaya, 2004). Brutia pine is valued for its resin and timber, and as an ornamental tree in landscaping. Its seeds are also used in pastry-making.
Brutia pine grows on all substrates and in most bioclimates of the Mediterranean region, from sea level up to 2 000 metres above sea level, with regional adaptations along its large distribution range (Kurt et al., 2012). This species is adapted to hot, dry climates and is often found in mixed forests. It is drought-tolerant, with fire-resistant cones, allowing it to successfully colonize dry, abandoned, and burned areas.
Η Brutia, η Καλαβριανή ή Τουρκική πεύκη (Pinus brutia) είναι ένα ταχέως αναπτυσσόμενο, μεσαίου μεγέθους, αειθαλές δέντρο που συχνά συνδέεται με τη συγγενή πεύκη της Χαλεπίου (Pinus halepensis). Το δέντρο είναι εγγενές στις περιοχές της ανατολικής Μεσογείου και του Αιγαίου της Τουρκίας, και υπάρχουν μικροί, απομονωμένοι πληθυσμοί κατά μήκος της ακτής της Μαύρης Θάλασσας της Τουρκίας και της Γεωργίας (Kurt et al., 2012). Το δέντρο καλύπτει μεγάλες εκτάσεις στις ακτές της Τουρκίας όπου είναι οικονομικά σημαντικό ως η κύρια πηγή ξυλείας και δασικής κάλυψης και φυτεύτηκε ευρέως για την προστασία του εδάφους και τους ανεμοφράκτες τη δεκαετία του 1930 έως τη δεκαετία του 1970. Το δέντρο χρησιμοποιείται ευρέως σε προγράμματα δάσωσης και αναδάσωσης στη νότια και δυτική Τουρκία, όπου καλύπτει το 24% της συνολικής δασικής έκτασης (Kandedmir, Kandemir, and Kaya, 2004). Το πεύκο Brutia εκτιμάται για τη ρητίνη και την ξυλεία του και ως καλλωπιστικό δέντρο στον εξωραϊσμό. Οι σπόροι του χρησιμοποιούνται και στη ζαχαροπλαστική.
Η πεύκη Brutia αναπτύσσεται σε όλα τα υποστρώματα και στα περισσότερα βιοκλίματα της περιοχής της Μεσογείου, από το επίπεδο της θάλασσας έως τα 2 000 μέτρα πάνω από την επιφάνεια της θάλασσας, με τοπικές προσαρμογές στο μεγάλο εύρος κατανομής της (Kurt et al., 2012). Αυτό το είδος είναι προσαρμοσμένο σε ζεστά, ξηρά κλίματα και απαντάται συχνά σε μικτά δάση. Είναι ανθεκτικό στην ξηρασία, με πυρίμαχους κώνους, που του επιτρέπουν να αποικίζει με επιτυχία ξηρές, εγκαταλειμμένες και καμένες περιοχές.
Σχετικές αγγελίες




Έλεγχος για ενημερώσεις στα Αγαπημένα

-
This account has a verified association with E-mongolia
-
Verified since
-
Your ad will be marked as verified
-
Advertising will receive more attention and trust